Brain Tumors are abnormal growths of cells within the brain or the surrounding tissues. They can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous)...
Brain Tumors are abnormal growths of cells within the brain or the surrounding tissues. They can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and they can arise from brain cells, the membranes that cover the brain (meninges), nerves, or glands. While the exact cause of most Brain Tumors remains unknown, certain risk factors may increase the likelihood of their development, including exposure to ionizing radiation, family history of brain tumors, and certain genetic conditions. Symptoms of brain tumors can vary widely depending on their location, size, and rate of growth, but common signs may include Headaches, seizures, changes in vision, hearing or speech difficulties, weakness or numbness in the limbs, balance or coordination problems, and cognitive or personality changes. Diagnosis of a Brain Tumor typically involves a combination of imaging tests such as MRI or CT Scans, followed by a biopsy to determine the type and grade of the Tumor. Treatment options for Brain Tumors depend on factors such as the type, size, and location of the Tumor, as well as the patient's overall health and preferences. Options may include Surgery, Radiation Therapy, Chemotherapy, Targeted Therapy, Immunotherapy, or a combination of these approaches. Supportive care and rehabilitation are integral components of treatment, aiming to manage symptoms, improve quality of life, and address physical and emotional needs. While the prognosis for Brain Tumors can vary widely depending on various factors, ongoing research and advancements in treatment offer hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for affected individuals. Early detection, prompt intervention, and access to comprehensive multidisciplinary care remain essential in the management of brain tumors, with continued efforts in research and awareness crucial in the fight against this complex and often challenging disease.
Facing a cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming. Our brief guide offers insights into various types of cancer, detailing symptoms, detection, treatments, and post-treatment care, providing support and clarity along your journey.
Risk Factors for Brain Tumors include exposure to ionizing radiation, family history of brain tumors, certain genetic conditions such as neurofibromatosis and Li-Fraumeni syndrome, and immune system disorders. While these factors may increase the risk of developing brain tumors, the majority of cases occur in individuals with no known risk factors.
The Signs and Symptoms of Brain Tumors vary depending on their location, size, and rate of growth. Common symptoms may include Headaches, seizures, changes in vision, hearing or speech difficulties, weakness or numbness in the limbs, balance or coordination problems, cognitive or personality changes, Nausea, Vomiting, and difficulty with daily activities.
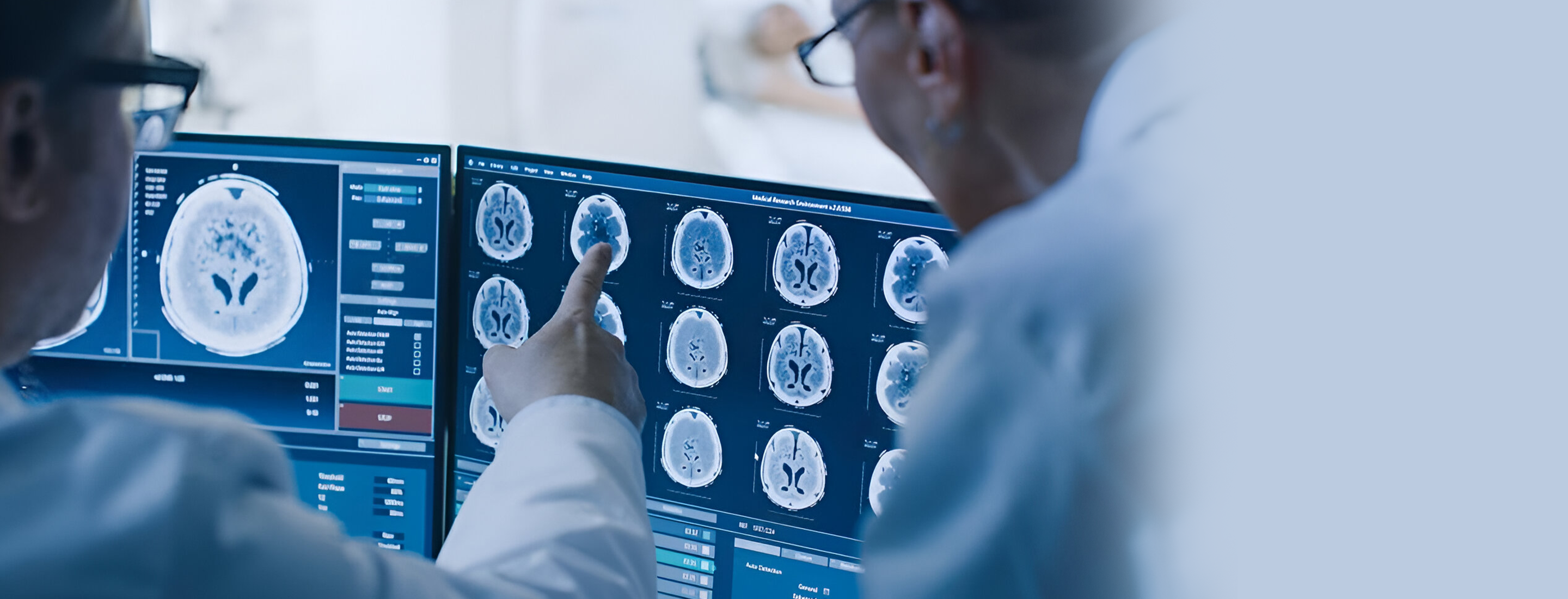
Diagnosing a Brain Tumor typically involves a combination of Imaging Tests such as MRI or CT Scans, which can visualize the tumor and its characteristics. A biopsy may be performed to obtain a tissue sample for analysis to determine the type and grade of the tumor. Additionally, neurological exams and other tests may be conducted to assess cognitive function, vision, hearing, and other neurological functions.
Treatment options for Brain Tumors depend on factors such as the type, size, and location of the tumor, as well as the patient's overall health and preferences. Options may include surgery to remove the Tumor, Radiation Therapy, Chemotherapy, Targeted Therapy, Immunotherapy, or a combination of these approaches. The choice of treatment is often individualized based on the specific characteristics of the tumor and the patient's goals of care.
Supportive Care and Rehabilitation are essential components of treatment for Brain Tumors, aiming to manage symptoms, improve quality of life, and address physical and emotional needs. This may include Pain Management, Physical Therapy, Occupational Therapy, Speech Therapy, Nutritional Support, Psychological Counseling, and assistance with activities of daily living.
Preventing Brain Tumors may not be entirely possible due to many cases occurring sporadically without identifiable risk factors. However, avoiding exposure to ionizing radiation, protecting the head from injury, and managing other health conditions that may contribute to tumor development may help reduce the risk.
Brain Tumors are complex and often challenging to treat, but advancements in diagnosis and treatment have improved outcomes for many patients. Early detection, prompt intervention, and access to comprehensive multidisciplinary care are crucial in managing brain tumors effectively. Continued research efforts are needed to better understand the underlying causes of brain tumors and develop more effective prevention strategies and treatments.
A Brain Tumor is an abnormal growth of cells in the Brain or its surrounding tissues. There are various types of Brain Tumors, including Gliomas (such as Glioblastoma Multiforme), Meningiomas, Pituitary Tumors, Metastatic Tumors, and Primary Brain Tumors.
Symptoms of a Brain Tumor may vary depending on its location and size but can include Headaches, seizures, changes in vision, difficulty speaking or understanding Language, Weakness or Numbness in the Limbs, Balance problems, and personality or behavior changes.
Diagnosis typically involves a Neurological examination, Imaging Tests such as MRI or CT Scans, and sometimes a biopsy to determine the type of Tumor and its characteristics.
Treatment options may include surgery to remove the Tumor, Radiation Therapy, Chemotherapy, Targeted Therapy, Immunotherapy, or a combination of these treatments. The choice of treatment depends on factors such as the type, size, and location of the tumor, as well as the patient's overall health.
Surgery may be recommended to remove as much of the tumor as possible, especially if it is causing symptoms or if it is accessible without causing significant risk to surrounding brain tissue. However, in some cases, other treatments such as Radiation Therapy or Chemotherapy may be used alone or in combination.
Risks of Brain Tumor Surgery may include Infection, Bleeding, damage to surrounding brain tissue leading to Neurological deficits, and complications related to anesthesia. Your Neurosurgeon will discuss the potential risks and benefits of surgery with you before the procedure.
Radiation Therapy uses high-energy beams to target and destroy Cancer Cells. It may be used as a primary treatment for inoperable tumors, as adjuvant therapy following surgery, or to shrink tumors before surgery.
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill Cancer cells or stop them from growing. It may be given orally or intravenously and can be used alone or in combination with other treatments for Brain Tumors.
Targeted Therapies are drugs that specifically target certain molecules or pathways involved in the growth and spread of Cancer cells. They may be used to treat specific types of Brain Tumors, such as those with specific genetic mutations.
Some patients may find relief from symptoms through complementary Therapies such as Acupuncture, Massage Therapy, meditation, or nutritional supplements. It's essential to discuss these options with your healthcare provider.
Yes, Brain Tumors can recur, even after successful treatment. Regular follow-up appointments and imaging studies are essential to monitor for any signs of recurrence.
The prognosis for Brain Tumor patients depends on factors such as the type, size, and location of the tumor, as well as the patient's age and overall health. Survival rates vary widely depending on these factors.
While there are no guaranteed ways to prevent Brain Tumors, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding exposure to carcinogens (such as tobacco smoke), and protecting the head from injury may help reduce the risk.
Offer emotional support, accompany them to medical appointments, help them research treatment options, and assist with daily tasks as needed. Encourage them to communicate openly with their healthcare team and seek support from friends, family, or support groups.
To schedule a consultation, please contact BMCHRC's Neurology or Neurosurgery department. Our team of specialists is dedicated to providing personalized care and support to patients with Brain Tumors, and we are here to help you through every step of your treatment journey.
Every contribution is a vital step forward in our battle against cancer, bringing hope and healing to countless lives. Join us in making a difference today.
Donate Now