At the Bhagwan Mahaveer Cancer Hospital & Research Centre (BMCHRC), our Nuclear Medicine represents the forefront of compassionate cancer care. We understand that a cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming, both physically and emotionally, which is why our dedicated team is committed to providing personalized and comprehensive care to every individual who walks through our doors.
Nuclear Medicine at BMCHRC offers cutting-edge diagnostic and therapeutic services for patients with various medical conditions, including cancer. Our dedicated team of nuclear medicine physicians and technologists utilizes advanced imaging techniques such as positron emission tomography (PET) and single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) to visualize physiological processes within the body at a molecular level. These non-invasive imaging studies provide valuable information for the early detection, staging, and monitoring of cancer, allowing for personalized treatment planning and targeted interventions. Additionally, our nuclear medicine department offers therapeutic options such as radioiodine therapy for thyroid cancer and radionuclide therapy for metastatic bone pain palliation. With a commitment to excellence and innovation, we strive to provide patients with the highest quality nuclear medicine services, contributing to improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
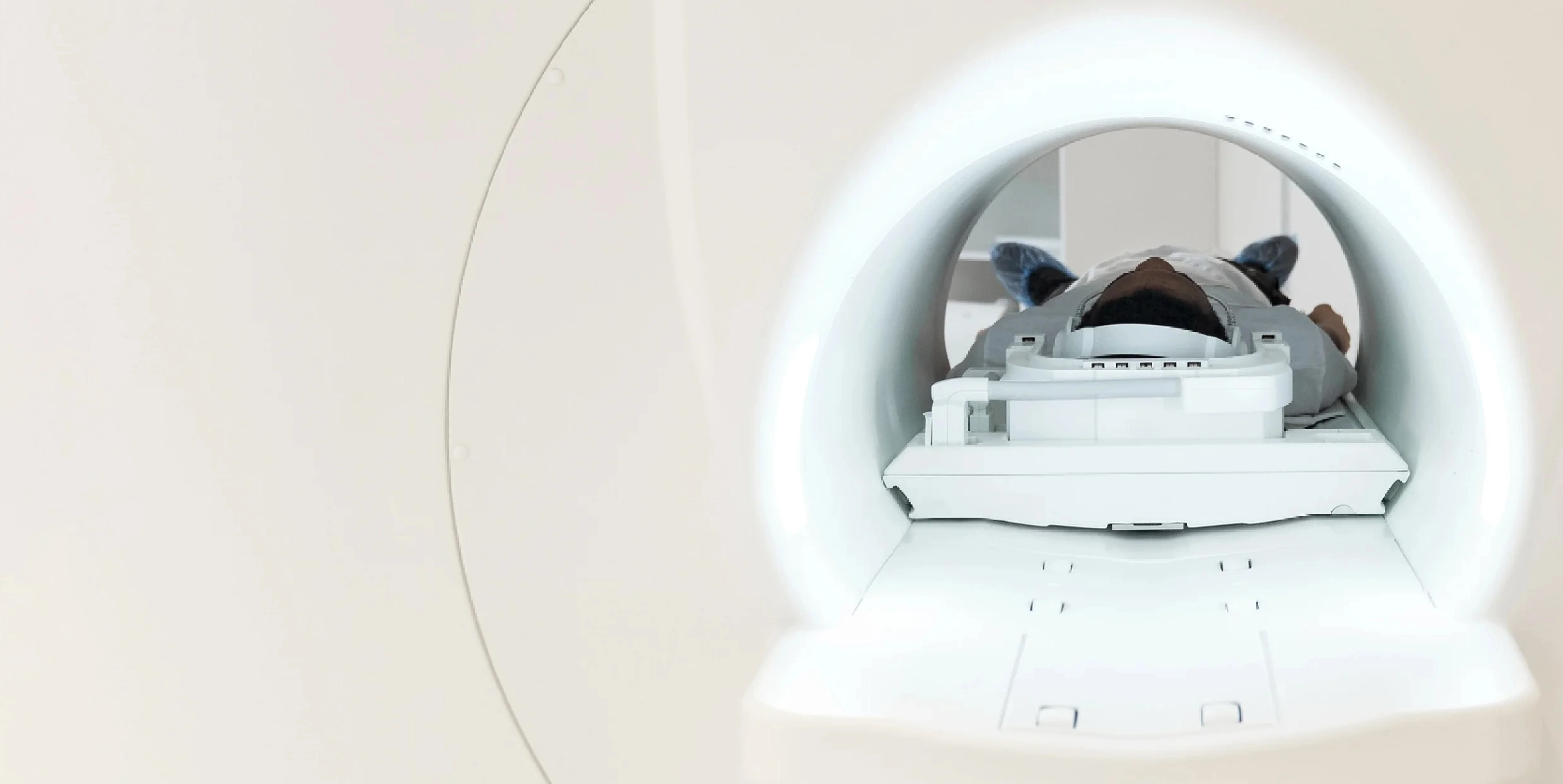
PET-CT, short for Positron Emission Tomography-Computed Tomography, is a hybrid imaging technique that combines the functional information from PET scans with the anatomical detail from CT scans. It provides comprehensive imaging by merging metabolic activity data from PET with structural information from CT, offering a more precise and detailed assessment of various medical conditions, especially cancer.
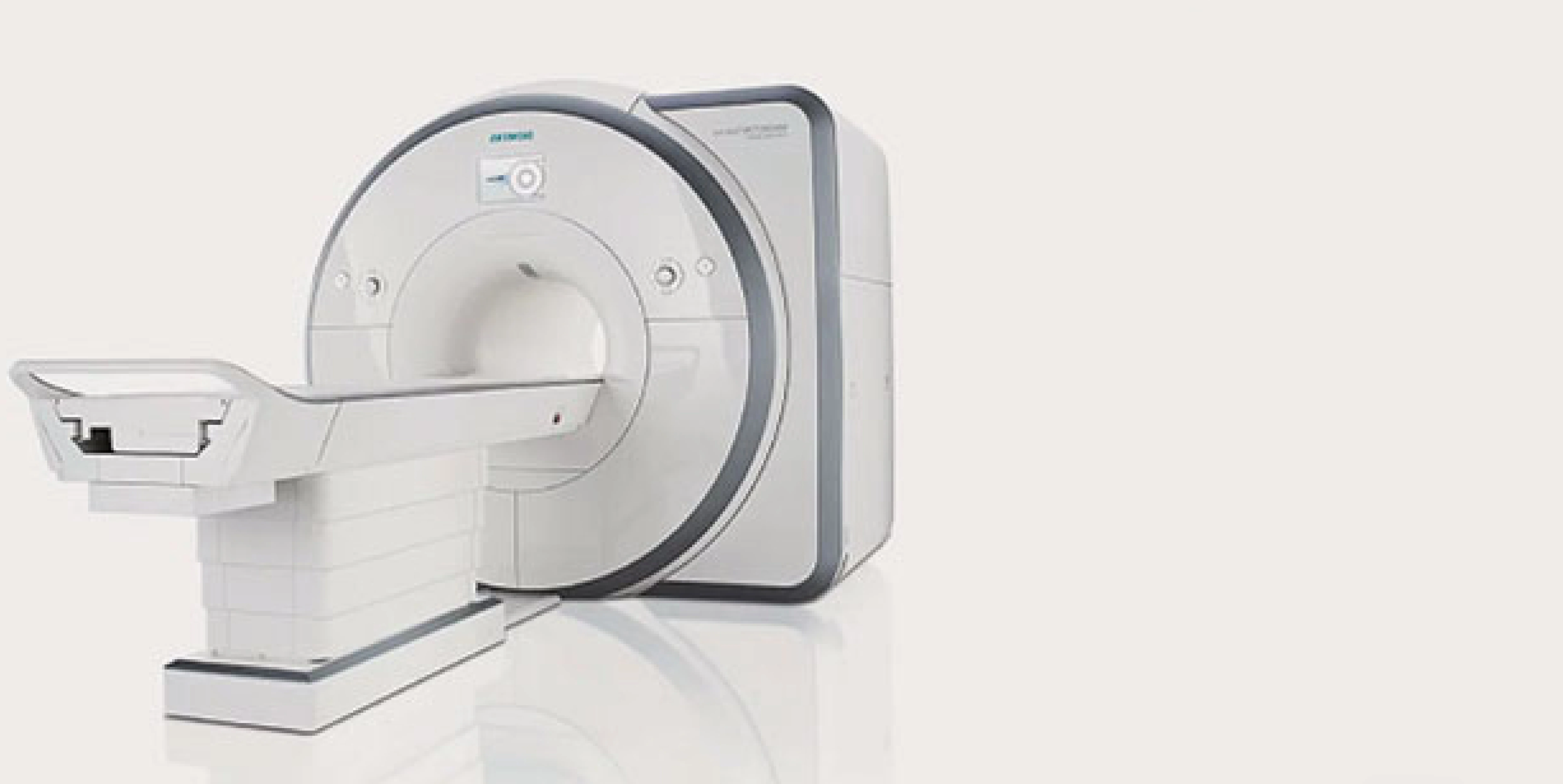
A Gamma Camera, also known as a scintillation camera or Anger camera, is a specialized imaging device used in nuclear medicine to detect and visualize gamma radiation emitted by radioactive substances (radiopharmaceuticals) within the body. It is an essential tool for diagnostic imaging procedures such as gamma scintigraphy, single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), and planar imaging in nuclear medicine.Despite these considerations, gamma cameras play a crucial role in nuclear medicine and diagnostic imaging, providing valuable insights into organ function, disease processes, and treatment responses.
Radioiodine Therapy, also known as radioactive iodine therapy or iodine-131 therapy, is a form of targeted radiation therapy used to treat thyroid conditions, particularly thyroid cancer and certain thyroid disorders. It involves administering a radioactive form of iodine, iodine-131 (I-131), which is selectively taken up by thyroid cells, including cancerous cells, due to the thyroid's natural iodine uptake mechanism. Radioiodine Therapy is a valuable treatment modality in managing thyroid disorders and thyroid cancer, offering effective disease control, minimal invasiveness, and customized treatment approaches.
Samarium Therapy, also known as samarium-153 (Sm-153) therapy or Samarium-153 Lexidronam therapy, is a type of targeted radiation therapy used in the treatment of painful bone metastases, particularly in patients with advanced cancer. Samarium-153 is a radioactive isotope that emits beta particles, which are used to target and destroy cancerous cells within the bone, providing pain relief and improving quality of life for patients with bone metastases.Samarium Therapy plays a valuable role in palliative care for patients with advanced cancer and painful bone metastases, offering effective pain relief, improved quality of life, and localized treatment of bone lesions. .

A Gallium-68 generator is a specialized device used in nuclear medicine to produce Gallium-68 (Ga-68), a radioactive isotope used in positron emission tomography (PET) imaging. Gallium-68 is particularly valuable for PET imaging because it has a relatively short half-life of about 68 minutes, allowing for rapid imaging studies while minimizing radiation exposure to patients. Despite these considerations, Gallium-68 generators and Ga-68 PET imaging have become integral components of advanced nuclear medicine and molecular imaging practices, providing valuable insights into disease processes, treatment responses, and personalized patient care.

PSMA (Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen) scan, also known as PSMA-PET scan or PSMA PET/CT scan, is a molecular imaging technique used in the diagnosis, staging, and management of prostate cancer. It combines positron emission tomography (PET) imaging with a radiotracer that specifically targets PSMA, a protein overexpressed on the surface of prostate cancer cells. The PSMA scan provides detailed information about the extent and characteristics of prostate cancer lesions, aiding in treatment planning and monitoring of disease progression. Despite these considerations, PSMA PET/CT imaging has revolutionized prostate cancer diagnostics and management, providing clinicians with valuable information for personalized treatment strategies, disease monitoring, and therapeutic decision-making.

The DOTA-NOC scan is a type of molecular imaging technique used in nuclear medicine for the detection and evaluation of neuroendocrine tumors (NETs). It involves the use of a radiopharmaceutical called DOTA-NOC, which is a somatostatin analog labeled with a radioactive isotope, typically Gallium-68 (Ga-68) or Fluorine-18 (F-18). The DOTA-NOC scan targets somatostatin receptors, which are often overexpressed in neuroendocrine tumor cells, allowing for the visualization and characterization of these tumors. Despite these considerations, DOTA-NOC PET/CT imaging plays a crucial role in the management of neuroendocrine tumors, providing valuable diagnostic information, guiding therapeutic strategies, and improving patient outcomes in the era of precision medicine and targeted therapies.

Sentinel Node Imaging is a specialized medical imaging technique used primarily in the context of surgical procedures, particularly in oncology, to identify and evaluate sentinel lymph nodes (SLNs). These nodes are the first lymph nodes that receive lymphatic drainage from a primary tumor site, and they play a crucial role in determining the extent of cancer spread (metastasis) in nearby lymph nodes and potentially distant organs. Sentinel node imaging aims to precisely locate and assess these sentinel nodes, aiding in surgical planning, staging, and treatment decisions. Despite these considerations, sentinel node imaging is a valuable tool in oncology, providing critical information about lymphatic drainage patterns, sentinel node involvement, and lymph node metastasis in various cancers.
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) is a targeted molecular therapy used in nuclear medicine for the treatment of certain types of neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) that express somatostatin receptors (SSTRs). PRRT combines a somatostatin analog (peptide) labeled with a radioactive isotope (radionuclide) to deliver radiation directly to tumor cells, specifically targeting cancer cells while sparing surrounding healthy tissues. This therapy aims to control tumor growth, alleviate symptoms, and improve quality of life in patients with advanced or metastatic neuroendocrine tumors.

Prostate Cancer is a type of Cancer that develops in the prostate gland, which is a small, walnut-shaped gland located below the bladder in men. The prostate gland produces seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. Prostate cancer typically grows slowly and remains confined to the prostate gland initially, but it can also be aggressive and spread to other parts of the body. The Prognosis for Prostate Cancer depends on various factors, including the cancer stage, grade, and overall health of the patient. Early detection and treatment can lead to favorable outcomes, especially for localized prostate cancer.
Neuroendocrine Tumors (NETs) are a diverse group of tumors that originate from neuroendocrine cells, which are found throughout the body but are concentrated in organs such as the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, pancreas, lungs, and adrenal glands. These tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous) and can arise in different parts of the body, producing various hormones or bioactive substances. NETs are characterized by their ability to secrete hormones, which can lead to distinct clinical syndromes and symptoms. The prognosis for Neuroendocrine Tumors varies widely depending on factors such as tumor type, stage, grade, hormone production, and response to treatment.
Meet our esteemed team of medical professionals, each equipped with years of specialized expertise and unwavering dedication to patient care.
Nuclear Medicine is a medical specialty that utilizes radioactive substances (radiopharmaceuticals) to diagnose and treat various medical conditions. Unlike traditional imaging techniques such as X-rays or CT scans, which rely on external sources of radiation, Nuclear Medicine involves the administration of radiopharmaceuticals that emit gamma rays or positrons, allowing for functional imaging of physiological processes within the body.
Nuclear Medicine can be used to diagnose and treat a wide range of conditions, including cancer, heart disease, neurological disorders, thyroid disorders, and bone disorders, among others. It is particularly useful for evaluating organ function, detecting tumors, assessing disease progression, and guiding therapeutic interventions.
During a Nuclear Medicine scan, a radiopharmaceutical is administered to the patient, either orally, intravenously, or through inhalation, depending on the specific procedure. The radiopharmaceutical emits gamma rays or positrons, which are detected by a specialized camera or scanner. The resulting images provide information about the distribution of the radiopharmaceutical within the body and the function of the targeted organ or tissue.
Nuclear Medicine procedures are generally safe when performed by trained professionals and in accordance with established protocols. The amount of radiation exposure from radiopharmaceuticals used in Nuclear Medicine scans is typically low and considered to pose minimal risk to patients. However, pregnant or breastfeeding women and young children may be advised to avoid certain Nuclear Medicine procedures unless absolutely necessary.
The duration of a Nuclear Medicine scan can vary depending on the specific procedure being performed. Some scans may take only a few minutes, while others may require several hours or even multiple sessions. The imaging time also depends on the uptake and clearance of the radiopharmaceutical within the body.
The preparation for a Nuclear Medicine scan depends on the type of procedure being performed. In some cases, patients may be instructed to fast for a certain period before the scan or discontinue certain medications. It is important to follow any pre-scan instructions provided by the healthcare provider or Nuclear Medicine technologist.
In general, Nuclear Medicine scans are not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women unless deemed absolutely necessary for medical reasons. Radiation exposure from the scan could potentially harm the developing fetus or be transmitted through breast milk to the infant. Alternative imaging modalities that do not involve radiation may be considered in such cases.
Common Nuclear Medicine procedures for cancer diagnosis and staging include positron emission tomography (PET) scans, bone scans, and radioiodine scans. PET scans are used to detect and evaluate the extent of cancerous lesions, while bone scans are used to detect bone metastases. Radioiodine scans are used to assess thyroid cancer.
Radioiodine Therapy, also known as Radioactive Iodine Therapy, involves the administration of radioactive iodine (iodine-131) to treat thyroid cancer. The radioactive iodine is selectively taken up by thyroid cells, including thyroid cancer cells, where it emits radiation that destroys the cancerous tissue while sparing surrounding healthy tissue.
Radiation exposure during Nuclear Medicine procedures is minimized through various safety measures, including the use of shielding devices, lead aprons, and collimators to restrict radiation exposure to the patient and healthcare providers. The amount of radioactivity administered is carefully calculated based on the patient's weight, age, and medical history to ensure the lowest effective dose is used.
Yes, Nuclear Medicine scans such as PET scans are capable of detecting cancer at an early stage by visualizing metabolic changes associated with tumor growth. PET scans can detect cancerous lesions before they are visible on conventional imaging modalities, allowing for earlier diagnosis and treatment initiation.
While Nuclear Medicine procedures are generally safe, there may be some risks and side effects associated with certain scans and treatments. These can include allergic reactions to radiopharmaceuticals, radiation exposure, and rare complications such as radiation sickness or thyroid damage. However, the benefits of the procedure usually outweigh the potential risks.
The frequency of follow-up Nuclear Medicine scans for cancer patients depends on factors such as the type and stage of cancer, the response to treatment, and the presence of any symptoms or new clinical findings. The healthcare provider will determine the appropriate follow-up schedule based on the individual patient's needs and circumstances.
Yes, Nuclear Medicine scans such as PET scans are commonly used to monitor response to cancer treatment by assessing changes in tumor size, metabolic activity, and disease progression over time. These scans can provide valuable information to healthcare providers regarding the effectiveness of treatment and the need for adjustments to the treatment plan.
To find a reputable Nuclear Medicine facility, you can ask your primary care physician or oncologist for recommendations. You can also research accredited healthcare institutions in your area that offer Nuclear Medicine services and inquire about their experience, expertise, and patient satisfaction ratings. Additionally, you can check with your health insurance provider to see if the facility is in-network and covered by your insurance plan.
Request a callback from our healthcare specialist